ClassNotFoundException与NoClassDefFoundError对比
文章目录
ClassNotFoundException与NoClassDefFoundError是Java开发中经常会遇到的异常与错误,本文基于个人工作中遇到的场景以及网上的资料,简要总结它们的差异、出现场景以及规避方案。
ClassNotFoundException
分析
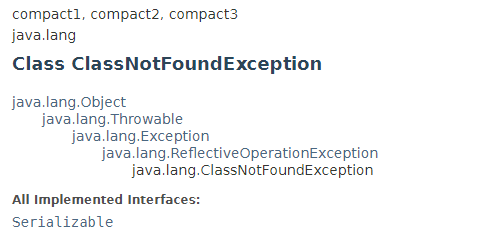
上图为ClassNotFoundException的类继承结构,从图中可看出它继承自Exception且没有继承自RuntimeException,基于Java语言规范它属于Checked Exception1,实际编程时必须在代码中利用try-catch显示的捕获处理或者利用throws将其抛出到上一层调用者处理,否则会导致编译器报错。
产生原因
在ClassNotFoundException的官方API中对于其产生的原因有如下描述:
Thrown when an application tries to load in a class through its string name using:
- The
forNamemethod in classClass.- The
findSystemClassmethod in classClassLoader.- The
loadClassmethod in classClassLoader.but no definition for the class with the specified name could be found.
基于上述描述可知ClassNotFoundException产生的根本原因如下:
在应用程序类中通过对应类的字符串名称去加载该类时找不到类的定义文件,即会抛出此异常
上述描述实际上可分为2类:
- 在
Class类中通过forName方法去加载类时找不到类定义文件,由于该方式可在普通的Java类中使用故较为常见(如加载数据库驱动) - 在
ClassLoader类中通过findSystemClass或loadClass去加载类时找不到类定义文件,由于是在类加载器中使用,一般的业务涉及较少故不常见
问题复现
-
基于
Class类的forName模拟复现:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16public class TestClassForName { public static void main(String[] args) { testForName(); } private static void testForName() { try { Class.forName("com.jdbc.mysql.Driver"); System.out.println("output info after Class.forName invoke inside try-catch"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("output info after Class.forName invoke outside try-catch"); } }输出结果如下,可见
try-catch之后的代码块还能正常执行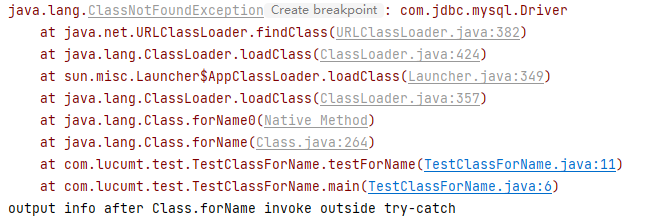
-
基于
ClassLoader中的loadClass复现:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16public class TestClassLoader { public static void main(String[] args) { testLoadClass(); } private static void testLoadClass() { try { ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass("com.jdbc.mysql.Driver"); System.out.println("output info after ClassLoader.loadClass invoke inside try-catch"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("output info after ClassLoader.loadClass invoke outside try-catch"); } }输出结果如下
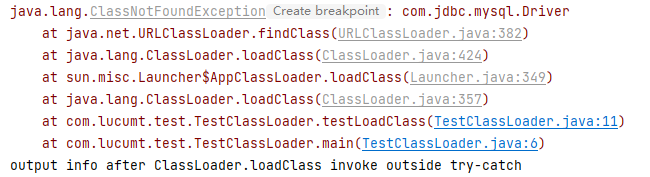
从上述结果可以看出ClassNotFoundException虽然会导致try-catch代码块里面位于异常发生点之后的代码无法执行,但是位于try-catch代码块外面的代码程序执行不受影响(这其实是Checked Exception自身的特性决定的)。
NoClassDefFoundError
分析
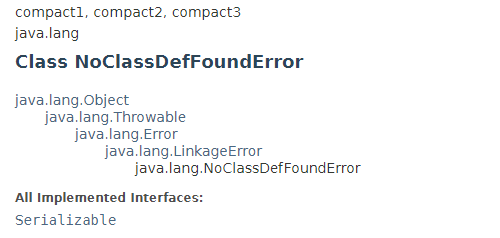
上图为NoClassDefFoundError的类继承结构,从图中可看出它继承自Error,,在Java语言关于Exception的官方API中有如下描述:
The unchecked exception classes are the run-time exception classes and the error classes.
故NoClassDefFoundError属于Unchecked Exception,而对于这类异常不需要在程序中显示的通过try-catch捕获,需要从代码和工程层面进行处理。
产生原因
在NoClassDefFoundError的官方API中有如下描述:
Thrown if the Java Virtual Machine or a
ClassLoaderinstance tries to load in the definition of a class (as part of a normal method call or as part of creating a new instance using thenewexpression) and no definition of the class could be found.The searched-for class definition existed when the currently executing class was compiled, but the definition can no longer be found.
基于上述描述可知NoClassDefFoundError产生的根本原因如下:
程序在编译时该类存在,在调用过程中JVM虚拟机加载该类时找不到该类的Class文件
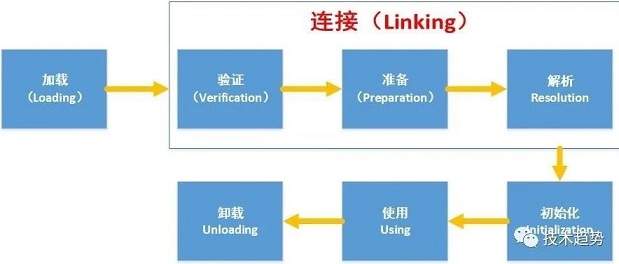
由于Java类加载过程有如下图所示的5个阶段,在其中每个阶段都可能会出现问题,结合实际开发场景,最典型的两类场景如下:
- 类加载阶段出错。如在编译时类存在,但执行时不存在,一个典型的场景是 jar包版本不匹配! 这也是我们开发过程中最容易遇到的场景
- 类初始化阶段出错。此种场景下编译也能通过,但由于某种原因导致初始化失败,程序仍然无法调用类。
与之相似的错误为NoSuchMethodError,其产生原因为程序执行时类存在,但是当前程序调用的方法不存在。
问题复现
-
类加载阶段出错,在编译后jar文件中删除要调用的class类即可实现:
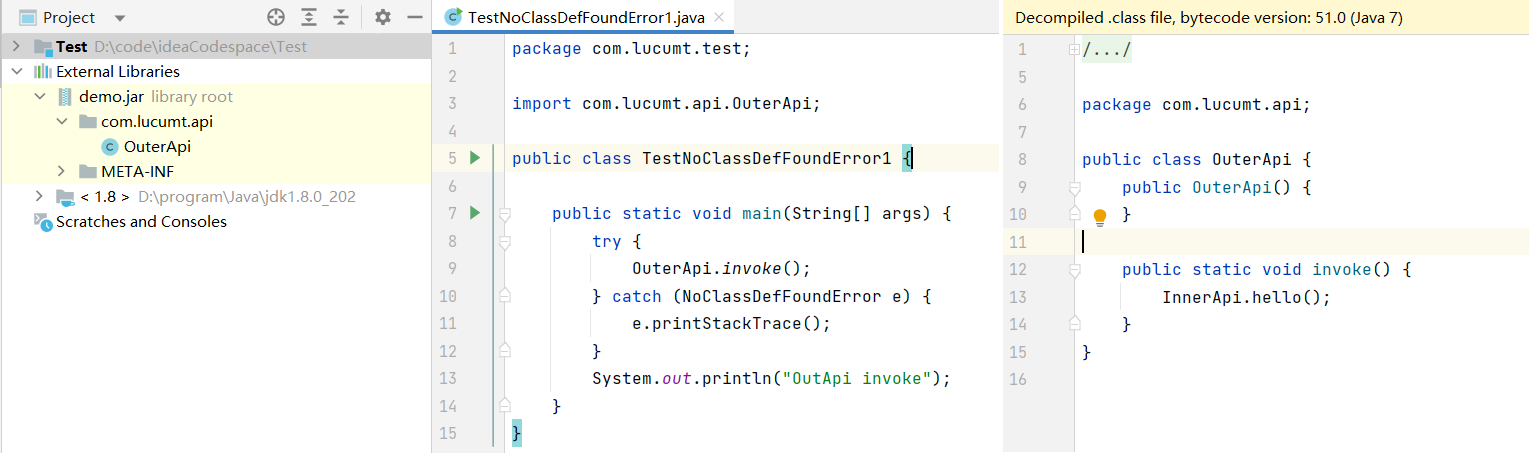
要编译为jar文件的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24/* 类结构 +---src | +---main | | \---java | | \---com | | \---lucumt | | \---api | | InnerApi.java | | OuterApi.java */ public class OuterApi { public static void invoke() { InnerApi.hello(); } } public class InnerApi { public static void hello() { System.out.println("hello"); } }主执行类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13import com.lucumt.api.OuterApi; public class TestNoClassDefFoundError1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { OuterApi.invoke(); } catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("OutApi invoke"); } }将上述工程编译打包为jar文件,然后在jar文件中去掉InnerApi,将其引入包含执行类的测试工程,此时其结构如下:
输出结果如下,可以看出虽然抛出了异常,但在
try-catch代码块之后的代码还是能够执行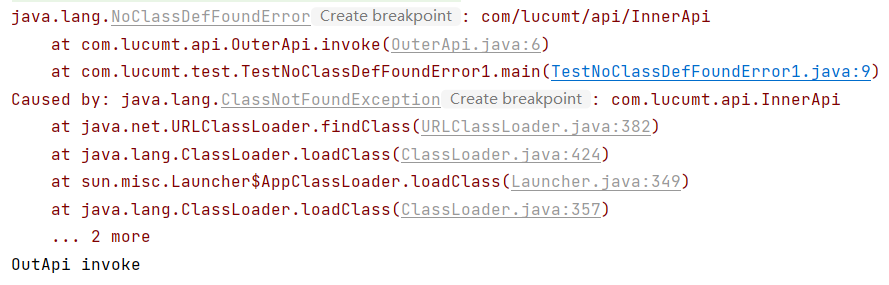
-
类初始化阶段出错,通过某种方式强制初始化出错:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20public class TestNoClassDefFoundError2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Demo.hello(); }catch(NoClassDefFoundError e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("invoke Demo.hello()"); } } class Demo { private static int val = 1 / 0; public static void hello() { System.out.println("hello"); } }输出结果如下,不同于前一个测试,此处的
try-catch之后的代码没有机会执行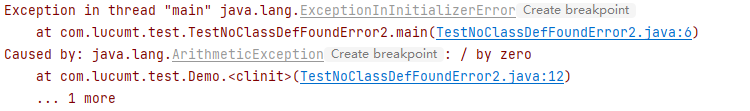
从上面2个实验中可发现虽然都对NoClassDefFoundError进行了try-catch捕获,但第一个能继续执行,而第二个却直接终止。造成这种差异的主要原因是第一个测试中的Demo没能完成初始化,导致整个程序加载失败(实际上程序提示的错误为 ExceptionInInitializerError),而第二个程序是在执行中才遇到类缺失2。
基于Unchecked Exception我们通常不需要在代码中显示的利用try-catch捕获,更多的是修改代码本身和调整jar文件版本。
总结
| ClassNotFoundException | NoClassDefFoundError | |
|---|---|---|
| 继承关系 | java.lang.Exception |
java.lang.Error |
| 类型 | 异常 | 错误 |
| 程序受影响程度 | 添加try-catch后可继续执行 |
基于产生于类加载的不同阶段,可能直接种植,也可能在try-catch之后继续执行 |
| 可能的场景 | 1.要加载的类不存在 2.类名编写错误 |
1.jar包缺失或jar包版本不匹配 2.类初始化失败 |
| 处理方法 | 1. 修改代码,添加缺失的jar文件 2. 代码中添加 try-catch捕获异常 |
修改代码业务逻辑 |
参考:
-
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se7/html/jls-11.html ↩︎
-
实际上应该有更科学更理论的解释,只不过自己目前找不到相关资料,暂时这么解释 ↩︎